What are the different types of auditors?

Here's What We've Covered!
What is the first thing that comes to your mind when you think of an auditor? Investigative, Inquisitive, Vigilant and sombre. The financial operations of a company are incomplete without being vetted by an Auditor. Conducting an audit is one of the most daunting tasks for an organization.
The role of an auditor involves huge responsibility. They examine the records of accounts and place a stamp of approval of the authenticity of the numbers. Not only does this involve accounting knowledge, but it also involves knowledge of areas like tax, laws, and financial regulations as well the minuscule demands of compliance norms.
Inspecting the books of accounts, however, is only one aspect of the auditor’s job. There are various aspects of an auditor’s role and there are various types of auditors with different auditing aims.
The most common types of auditors are:
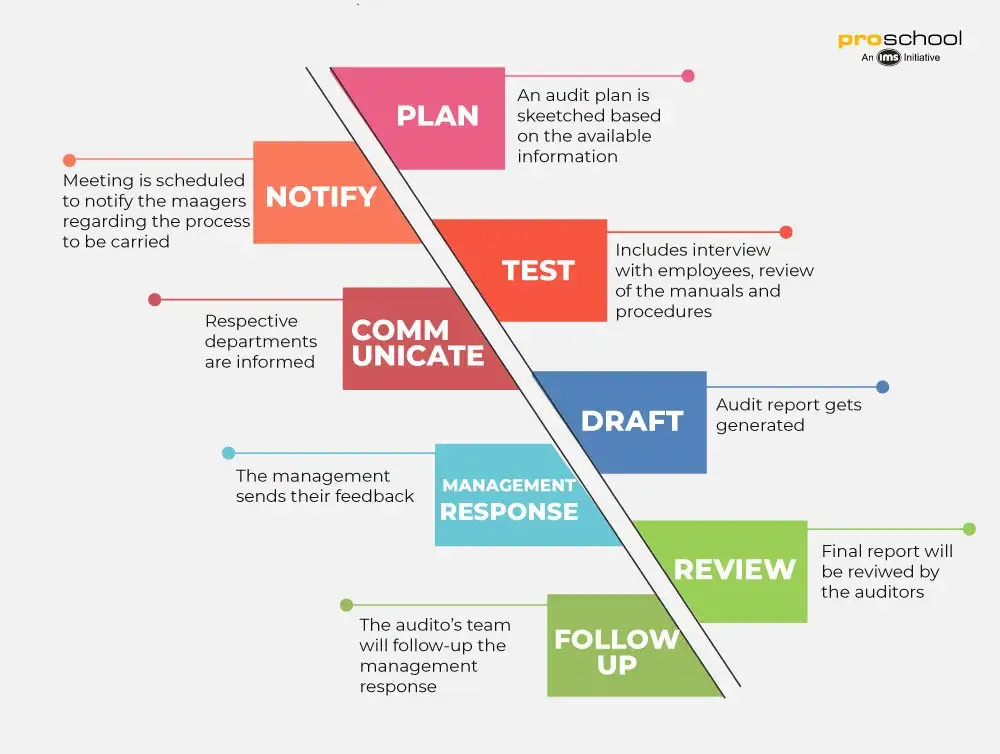
External Auditor: The most common type of auditor is the external auditor. He is asked to come to an institution or company and conduct an audit according to regulatory norms. An external auditor is expected to conduct an unbiased opinion and present an independent report.
He conducts the audit once a year and he has no affiliation with the company. The work of external auditors is crucial and he is answerable to the investors and government bodies.
An external auditor may have to communicate with the internal auditors but they are not influenced by the internal auditors. An External auditor may also have to coordinate with other departments such as technology or operations if he is doing a department focussed audit.
Government Auditor: Government Auditors are those who audit the financial position of Government agencies and private businesses involved in activities pertaining to government regulations, taxation, foreign exchange, etc.
Most of the Government Auditors are associated with audit firms which cater only to the public sector. The main role of the Government Auditors is to ensure that the finances are spent and earned according to the stipulated laws and rules. They conduct a high-quality audit that holds their clients accountable for the use of public resources in compliance with laws and regulations. Some of the functions performed by the Government Auditors are:
- Readiness for Audit
- Examination of the report
- Financial statement audits
- Compliance audits
- Performance audits
- Internal control testing
- Information system control audits
Do you know you can become an auditor after completing the ACCA course?
Internal Auditors:
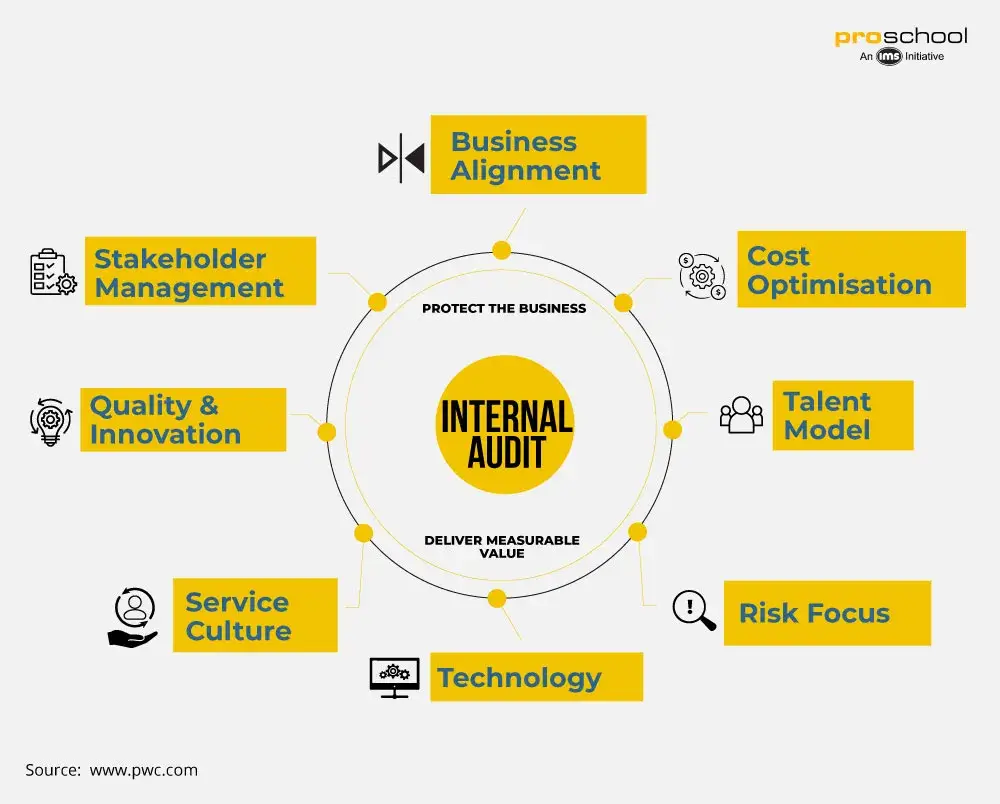
An internal auditor is someone who acts independently to assess the efficiency of a company’s internal control structure. Internal Auditors report to a company’s board or executives. They don’t just look at the financial statements but the overall risk management process to see which area needs improvement and redesigning.
The roles and responsibilities of an internal auditor are to collect, analyze and scrutinize all the company records to check if they are complying with all the regulations and managing the risk accordingly. They also perform an audit on all the systems, processes and internal controls. They may also do some value-additions to reduce the management costs, optimize resources and mitigate overall risk.
Once they complete the internal audit, they will submit the findings report to the board of executives for the final recommendations.
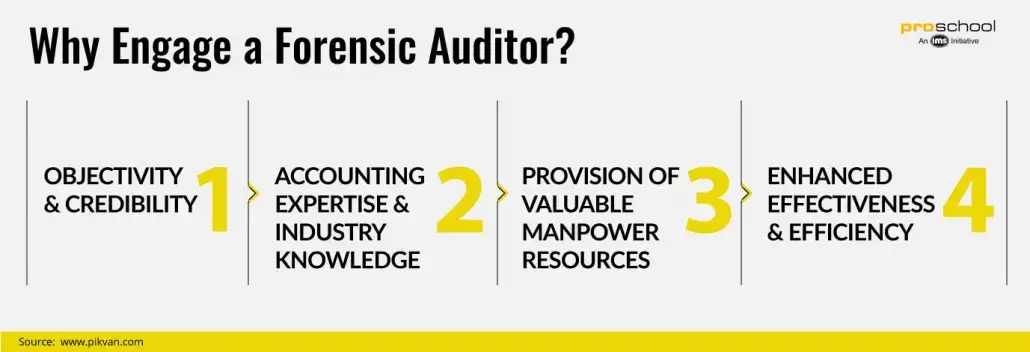
Forensic Auditor:
They are one of the most specialized kinds of auditors. Forensic Auditors are akin to external auditors in their functions but the purpose of their audit is very specific. This audit is performed as a part of certain legal proceedings. The audit report is a part of the report that needs to be submitted as evidence. The Forensic auditor may conduct the audit to impeach a party against crimes such as embezzlement, fraud or any other criminal activity. The key objectives for a Forensic Auditor are:
- Identifying if any fraud is being carried out
- Determining the period of fraud
- Investigating how the fraud was conducted in secrecy.
- Estimating the amount of loss that may have occurred.
- Gathering accurate evidence to be produced in court
- Recommending measures to prevent these frauds
Being a specialized field of audit, Forensic auditors must possess expert knowledge in multiple areas:
- Accounting
- Criminology
- Law
- Investigative Auditing
- Computer Science
- Data Analytics
- Machine Learning
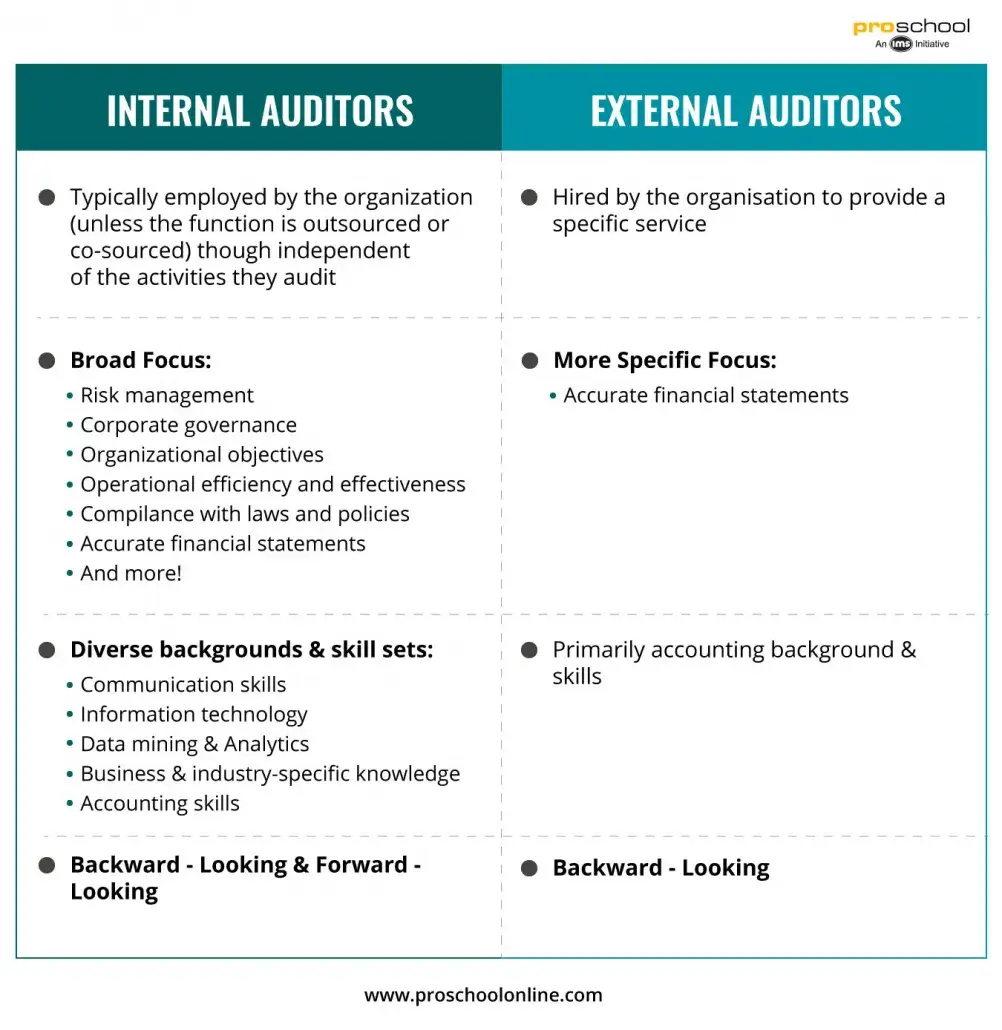
Difference between Internal Auditors and External Auditors:
Read more: How To Become An Accountant? Must Read For Indian Graduates
Resent Post
>
Best Study Abroad Courses for Commerce Graduates
>
Emerging commerce career options in India (2026): From CA to Data Analyst
>
ACCA Opportunities You Didn’t Know About – Think Beyond Audit!
>
Which Courses After 12th Commerce With High Salary Are in Demand Worldwide?
>
How to Find ACCA Jobs Online After Qualifying: Real Portals, Tips & Career Guidance
Follow Us For All Updates!
One Comment





This blog provides a clear breakdown of the various types of auditors and their roles, which is essential for understanding the auditing process.